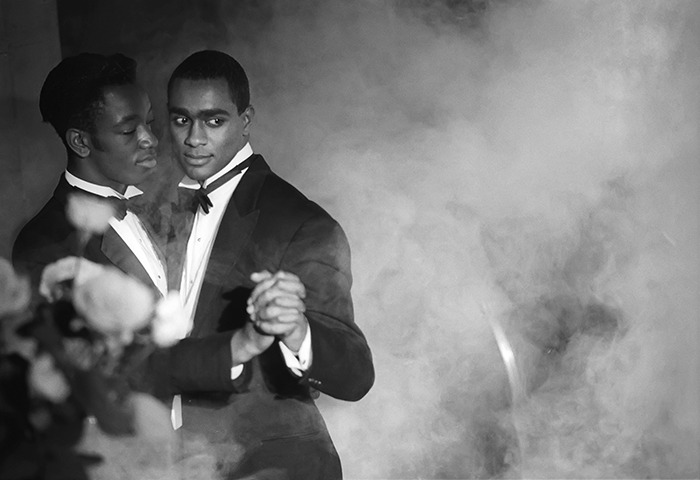E.L. Wiegand Gallery | Floor 2
Earl and Wanda Casazza Gallery | Floor 2
Ina Mae and Raymond Rude Gallery | Floor 2
Small Works Gallery | Floor 2
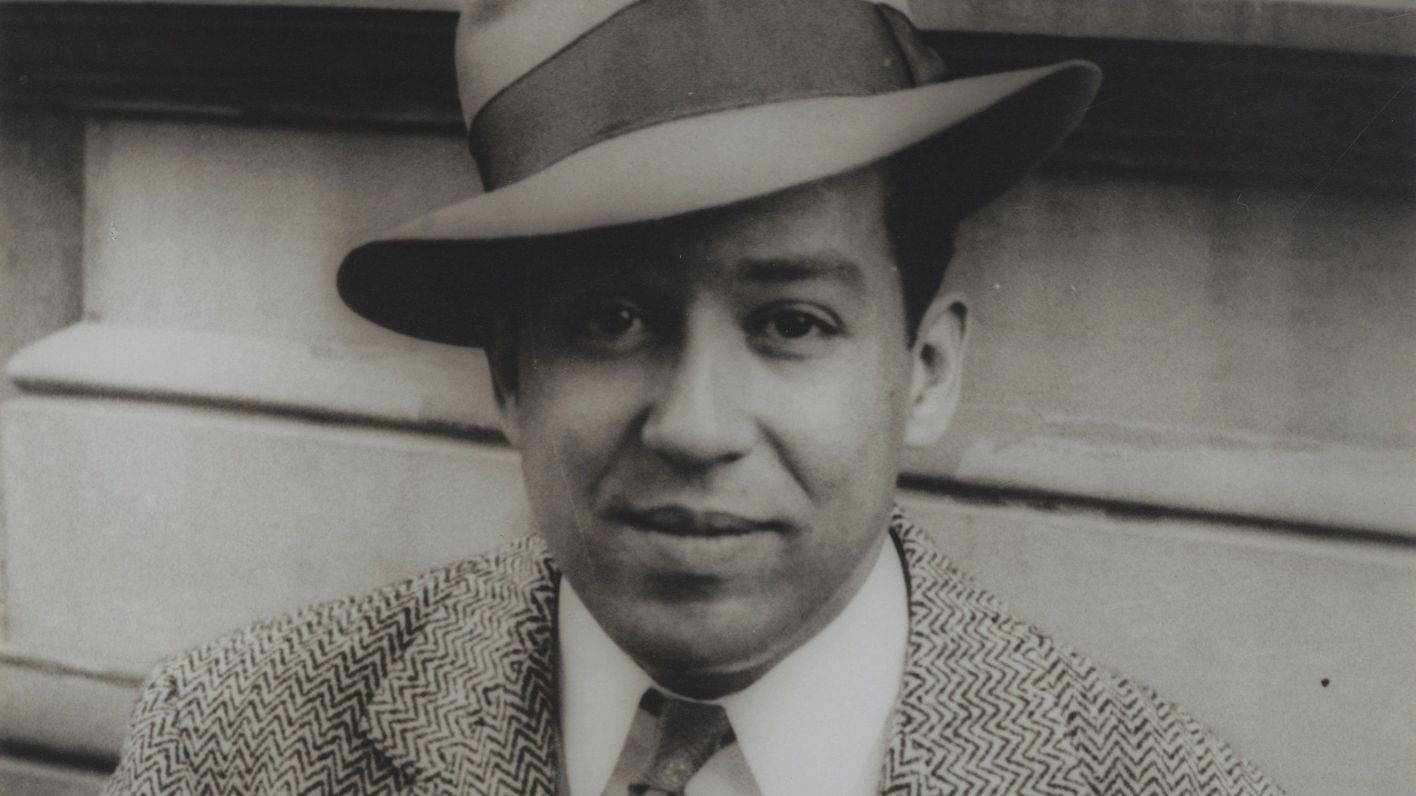
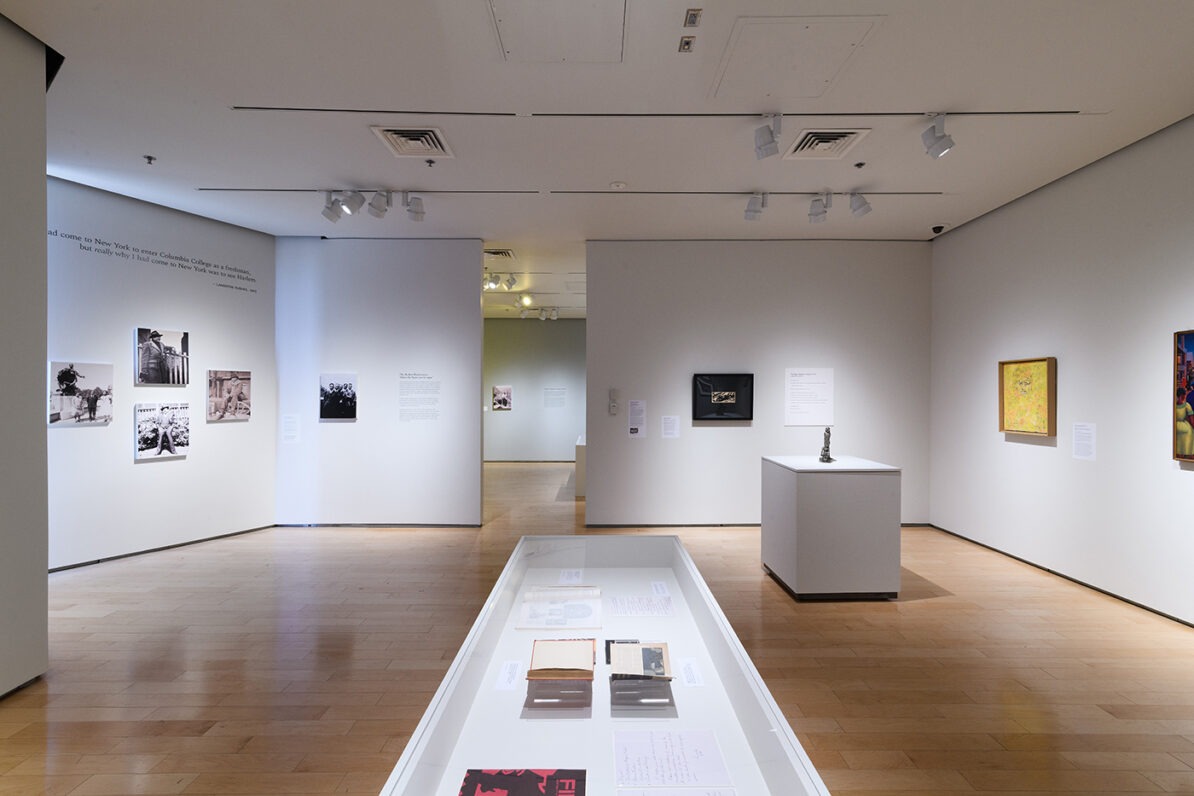
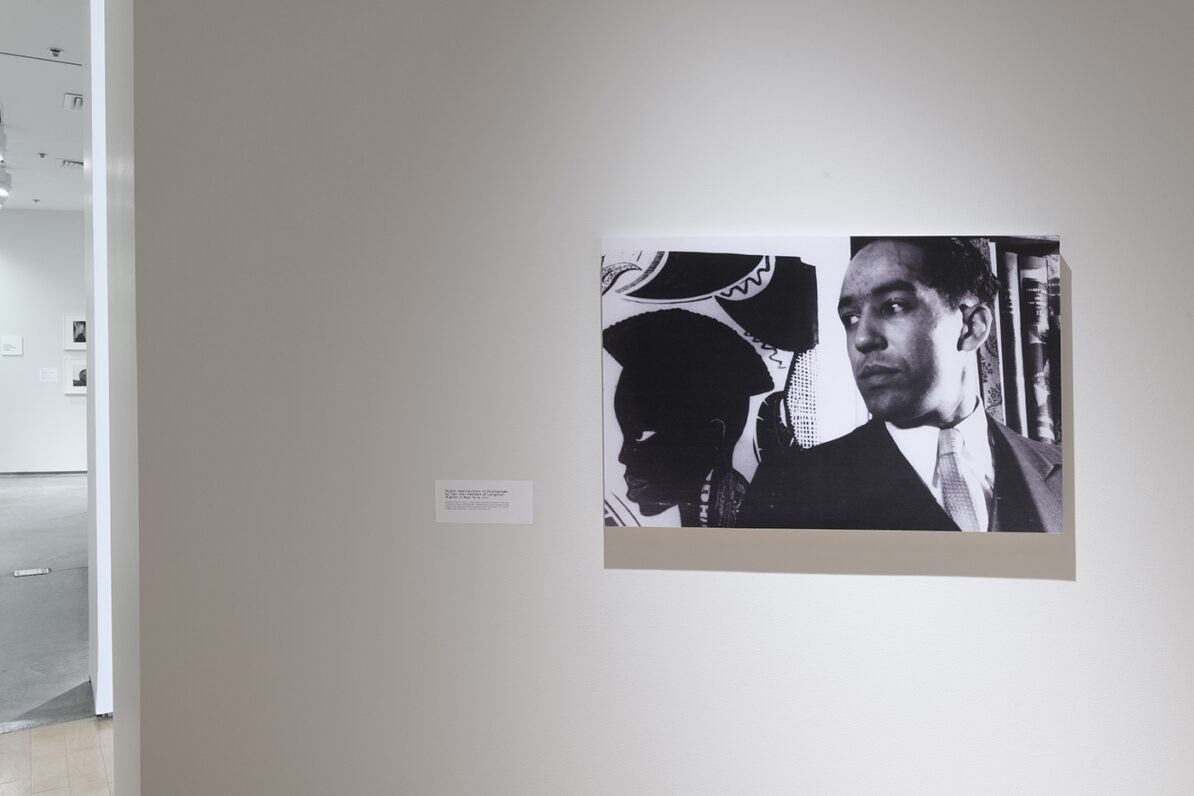
When Langston Hughes Came to Town explores the history and legacy of Langston Hughes through the lens of his largely unknown travels to Nevada and highlights the vital role Hughes played in the Harlem Renaissance and beyond. James Mercer Langston Hughes (1901-1967) was born in Joplin, Missouri. Hughes studied at Columbia University in 1921 for one year and would eventually become one of leading writers of the Harlem Renaissance. A writer with a distinctive style inspired by jazz rhythms, Hughes documented all facets of Black culture but became renowned for his incisive poetry.
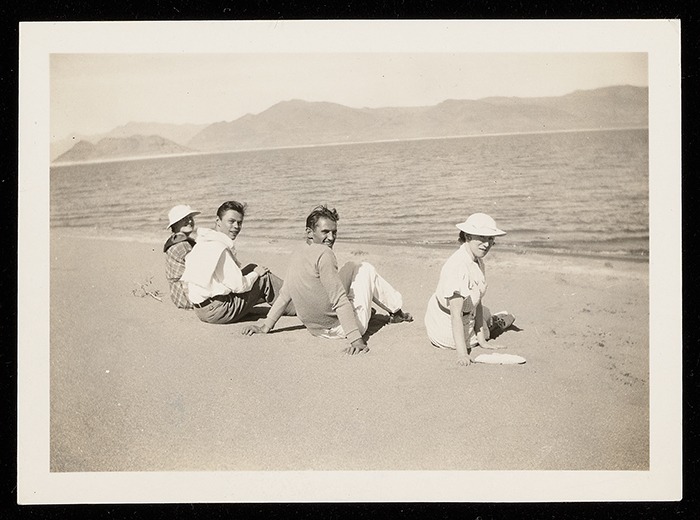
The exhibition begins by examining the relationship of this literary giant to the state of Nevada through a unique presentation of archival photographs, ephemera, and short stories he wrote that were informed by his visit to the area. The writer’s first trip to the Silver State took place in 1932, when he investigated the working conditions at the Hoover Dam Project. He returned to the state in 1934, at the height of his career, making an unexpected trip to Reno, and found solace and a great night life in the city.
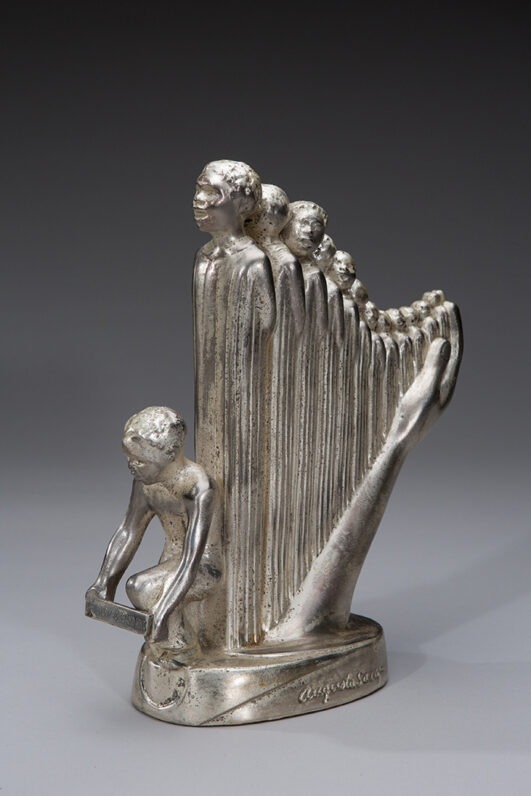
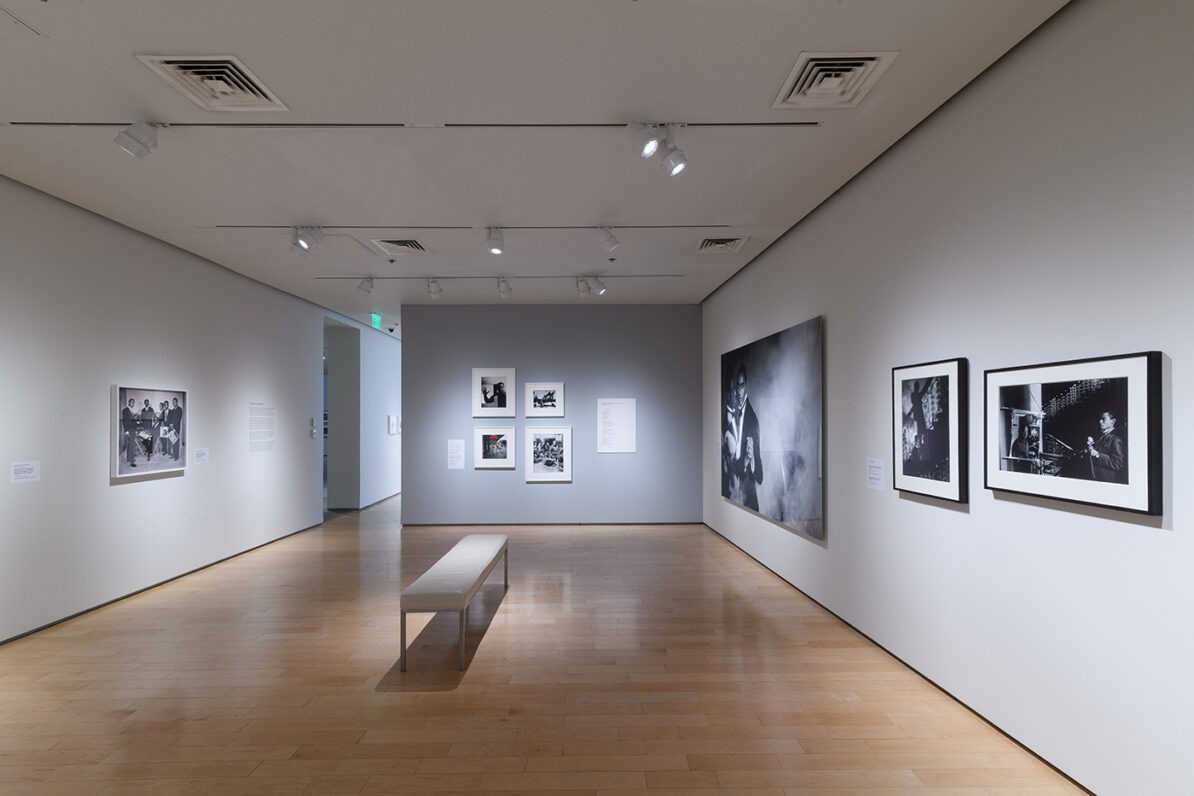
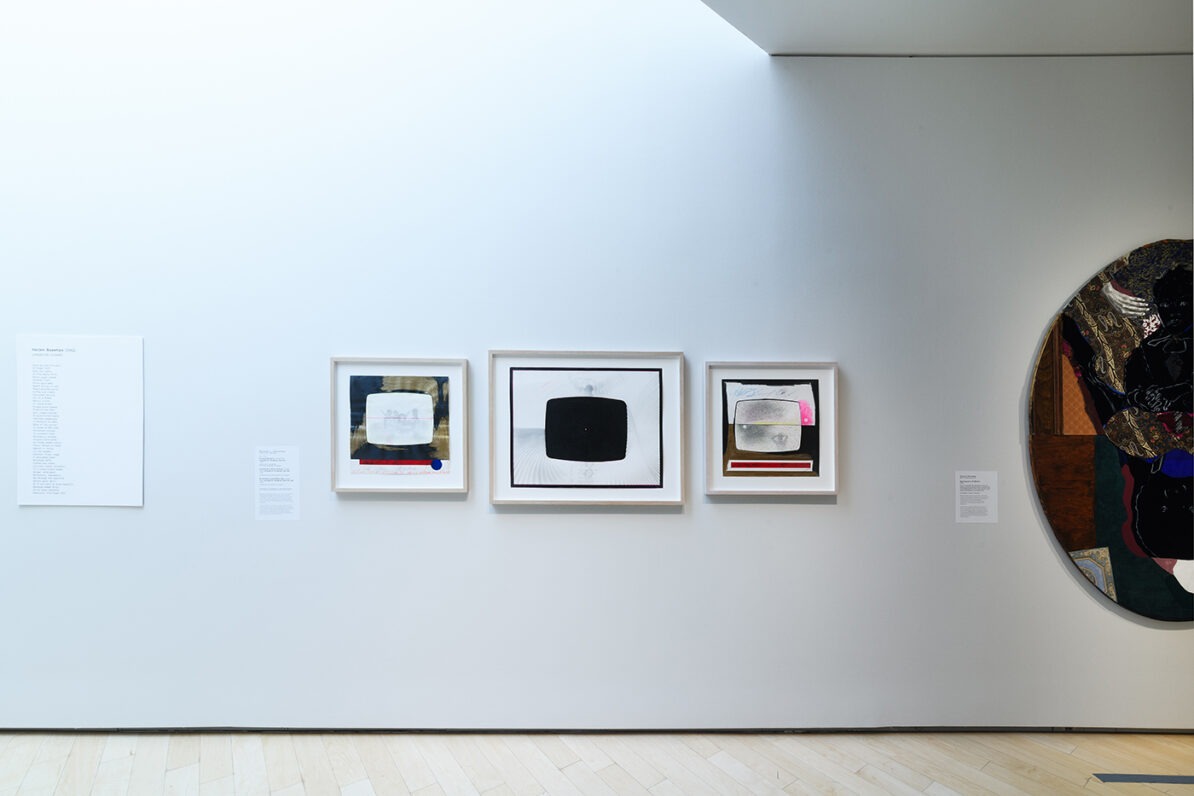
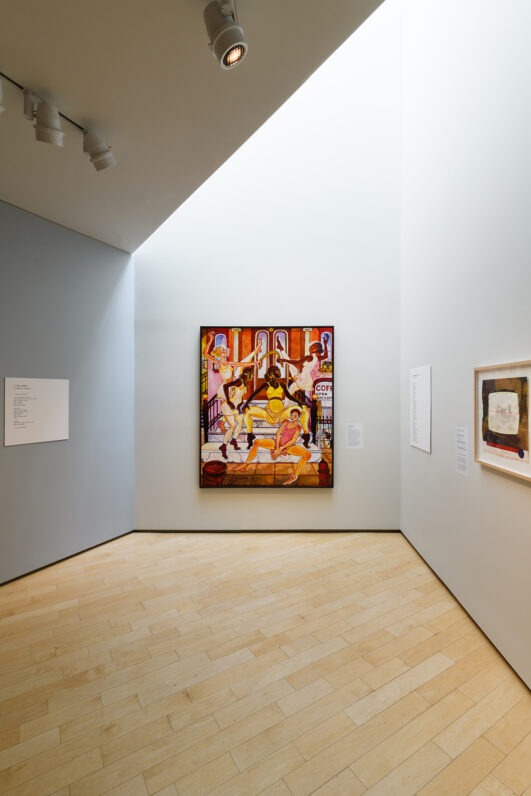
The presentation continues with work created by leading artists of the Harlem Renaissance who had close ties to Hughes, including sculptures by Augusta Savage and Meta Vaux Warrick Fuller, photographs by Griffith J. Davis, and paintings by Beauford Delaney, Romare Bearden, Aaron Douglas, Norman Lewis, Hugo Gellert, Hale Woodruff, Charles Alston, and Archibald J. Motley, Jr. The range of work on display foregrounds the rich expressions of dance, music, and fashion prevalent during the influential movement.
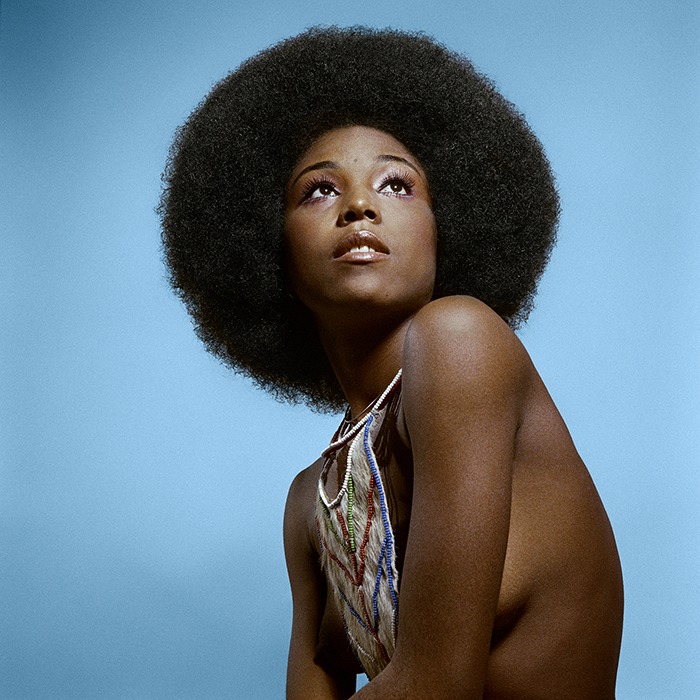
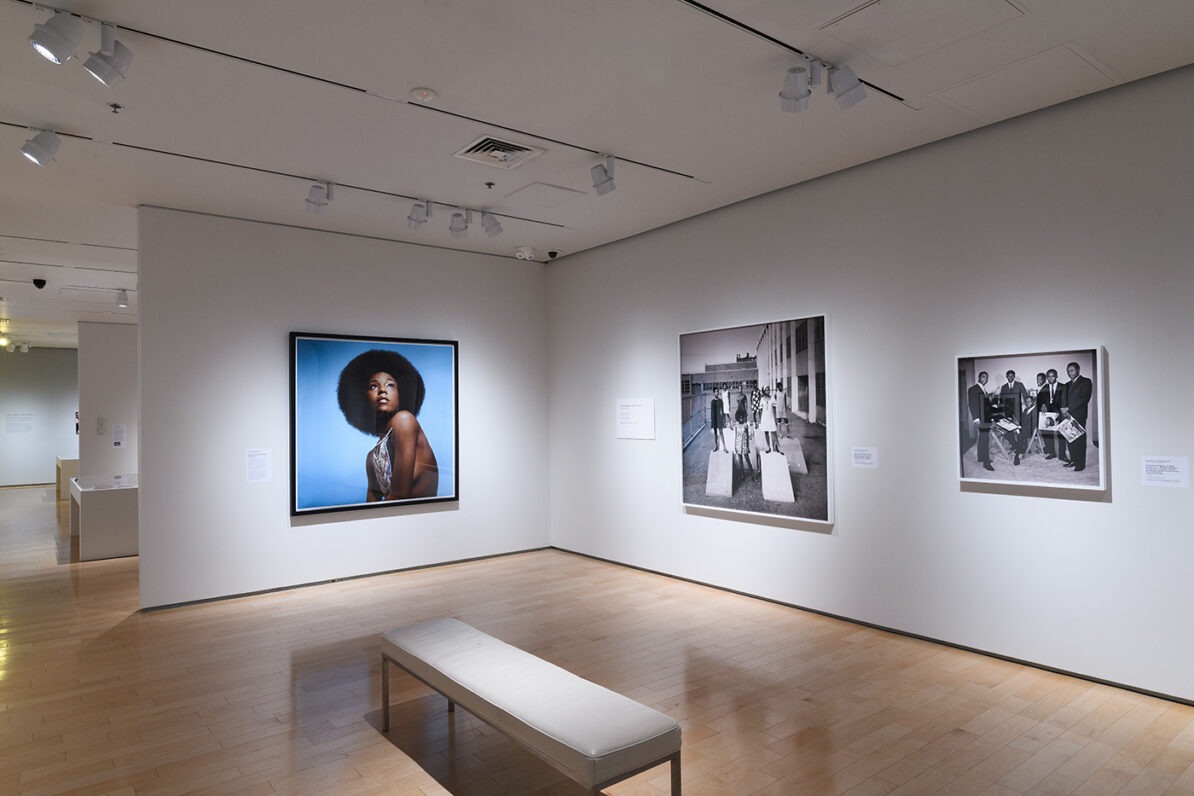
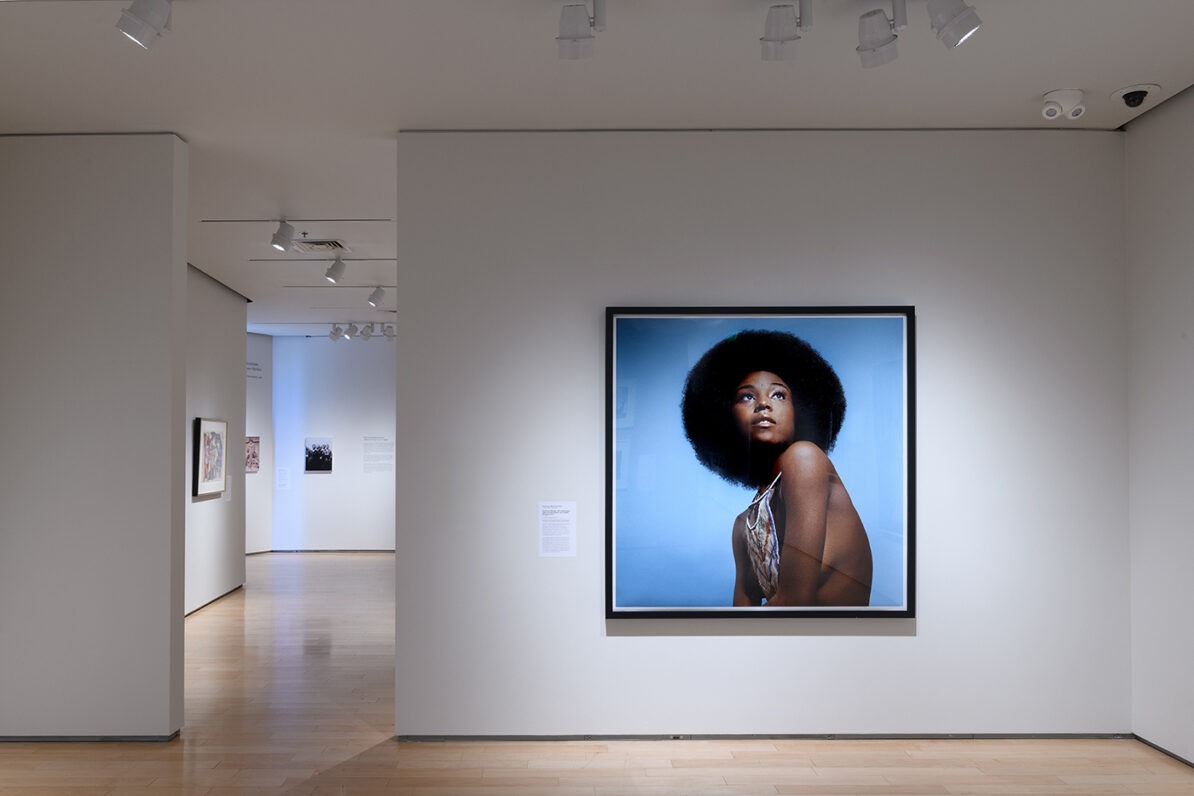
The final section of the exhibition features contemporary artists who were inspired by Hughes and made work about his life. Excerpts from Hughes’s poems and short stories are juxtaposed with related works of art, demonstrating how his legacy endures in the twenty-first century. Isaac Julien, Kwame Brathwaite, Deborah Willis, PhD., Benny Andrews, Gordon Parks, Chase R. McCurdy, Arvie Smith, and David Shrobe are the artists whose works are included. Julien, for example, in his renowned series Looking for Langston reimagines scenarios of Hughes’s life in Harlem during the 1920s. His black-and-white images are paired with Hughes poem “Poem (To F.S.).” Similarly, Brathwaite’s impactful photographs highlight the continuation of the Harlem Renaissance through the Black pride movement of the 1960s and are coupled with the poem “My People.” Finally, Glenn Ligon’s prints from his America neon sculptures relates to Hughes’s poignant poem “Let America Be America Again,” which leave viewers to ponder the question of belonging in America.
This exhibition is organized by the Nevada Museum of Art and curated by Carmen L. Beals, Associate Curator and Outreach Director, Las Vegas.
Major Sponsors
Thomas Lee Bottom
The Bretzlaff Foundation
Carol Franc Buck Foundation
Sponsors
Victoria and Victor Atkins
CEJohnson Foundation
The Deborah and T.J. Day Foundation
Nancy and Harvey Fennell | Dickson Realty
Hazel Foundation Fund
Jackie and Steve Kane
Chica Charitable Gift Fund
Sandy Raffealli
Phil and Jennifer Satre
Gayle and Cliff Scheffel
Elizabeth and Henry Thumann
Christine and Scott Tusher
Supporting Sponsors
Kathie Bartlett
Betsy Burgess and Tim Bailey
Mary Connolly
Tammy and Michael Dermody
Molly and Mark D. Gamble
Viki Matica and Doug Brewer
Charlotte and Dick McConnell
Keith McWilliams | Evercore Wealth & Trust
Peter E. Pool